X-LINKED DOMINANT
Here the mutant gene is dominant and is on the X chromosome. Males may be normal or affected and the female heterozygotes are more variably affected due to random inactivation of one X and severely affected when both X chromosomes carry it.
CRITERIA
- Affected males never transmit it directly to sons, but do transmit the gene to all their daughters. Fig. 32a.
- Affected heterozygous females transmit it to half their sons and half their daughters.
- There are more females than males, and in some conditions it is lethal in the male. Fig. 32a.
- Affected heterozygous females show a variable clinical picture due to random inactivation of one X.
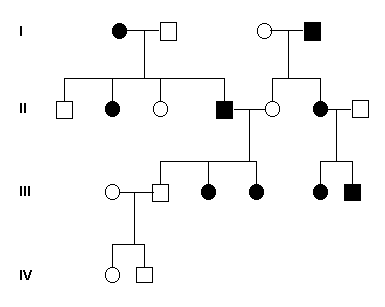
Fig 32a
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
- Vitamin D resistant rickets (hypophosphataemic rickets) appears at around 6 months of age when serum phosphorus levels drop. Diminished tubular resorption of phosphorous and reduced gut resorption of calcium and phosphorous contribute to X rays showing bowing of lower limbs, slow growth with short stature and a waddling gait.
- Incontinentia pigmenti and Rett syndrome in males are lethal and only females survive. The Xg blood group is a normal trait inherited in this manner.